
Wind is a major force in propelling water across the globe in surface currents. Gravity pulls the water away from hills and toward valleys and Earth’s rotation steers the moving water. The Sun’s radiation creates prevailing wind patterns, which push ocean water to bunch in hills and valleys. Climate change is altering the processes that propel water across the globe, and should this alter ocean currents, it would likely lead to a cascade of even more change.Īt the surface, currents are mainly driven by four factors-wind, the Sun’s radiation, gravity, and Earth’s rotation. While the ocean as we know it has been in existence since the beginning of humanity, the familiar currents that help stabilize our climate may now be threatened. This planetary movement has a strong effect on how oceans move. Though it appears we live on a stable and stationary planet, we are, in fact, whipping through space around the Sun in an orbit and spinning on an axis. It also requires a shift in perspective to encompass the movement of planets, the Moon, and the Sun. Ocean motion is influenced by occurrences here on Earth that are familiar, like heat changes and wind. Friction, drag, and density all come into play when describing the nature of a wave, the movement of a current, or the ebb of a tide. Ocean movement is created by the governing principles of physics and chemistry. Water is propelled around the globe in sweeping currents, waves transfer energy across entire ocean basins, and tides reliably flood and ebb every single day. But this is far from the truth-the ocean is constantly in motion. So, the times for high and low tides change by 50 minutes each day.Looking toward the sea from land, it may appear that the ocean is a stagnant place.
Isaac Newton first explained tides scientifically in 1686.Neap tides occur during the quarter moon phase. "Neap tides" are weak tides that occur when the gravitational forces of the moon and the sun are perpendicular to one another, pulling on the Earth from different directions. During this time, the moon is between the Earth and the sun. The Proxigean Spring Tide is a rare, very high tide that occurs when the moon is unusually close to the Earth and in a new moon phase.
MOON PLANET INFLUENCE OCEAN TIDE GRAPH FULL
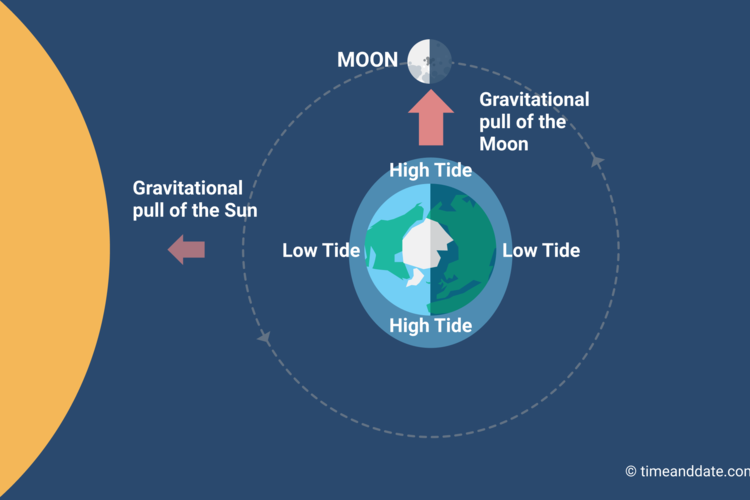
Spring tides occur during the full moon and new moon phases. Spring tides are strong tides that occur when the Earth, the moon and the sun are in a line.ĭuring these times, the combined gravitational pull of the moon and the sun is very strong. There are a few different types of special tides that occur depending on the phase of the moon. Meanwhile, on the other side of the Earth, there is another high tide created by the moon slightly pulling the Earth away from the still water on that side. As the moon's gravity pulls on the Earth, it pulls water into a bulge on the side closest to it.
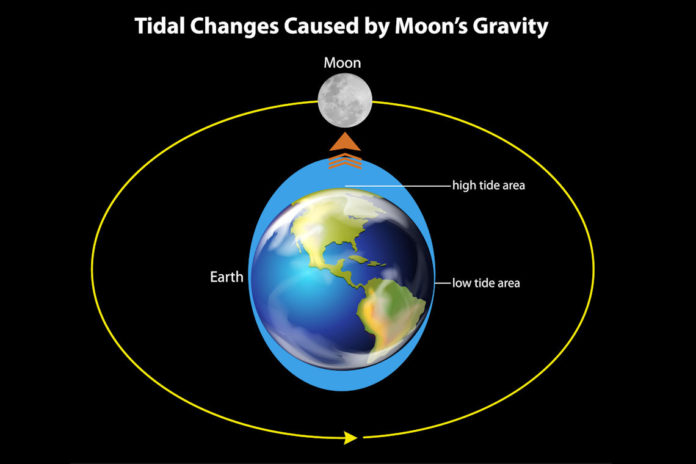

You might think that the opposite side of the Earth would experience a low tide, but that would be incorrect!Īmazingly, the moon's gravity creates a high tide on both sides of the Earth. The moon's gravitational force pulls on water in the oceans and causes bulges that create “high tide." The moon's gravitational pull is strongest on the side that faces the Earth. The sun is huge, but it is 360 times farther from the Earth than the moon.Įven though the moon is much smaller than the sun, it has two times more influence on tides than the sun, simply because it is much closer to the Earth. Tides are caused by gravitational forces of the moon and the sun. Large lakes, such as the Great Lakes, also have tides, but the change in water level is only inches. The word “tides" describes the regular rising and falling of the ocean's surface.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
